
If your passport has a small gold camera symbol on the front cover, you already have a biometric passport or e-passport. Inside that symbol is a tiny electronic chip that has your details and a digital version of your photo. This chip will help border officers (and e-gates) confirm that you’re really you. Most US passports issued within the past decade are biometric passports. Many countries now design their border control systems to match the vast majority of travelers holding an e-passport.
What is a Biometric Passport?
A biometric passport is a modern passport with an electronic chip that stores:
- Your basic personal details including:
- name
- nationality
- date of birth
- passport number
- expiry date
- A digital version of your passport photo
- In some countries, biometric data also includes fingerprints or Iris information (similar to a retinal scan)
Border officers and automated e-gates can read the chip and compare your biometrics to the data stored on it. Normally the system matches your face to your digital passport photo. Biometric passports in general makes border checks faster and more secure compared to old paper passports.
Distinguishing a Biometric Passport
You can check whether your passport is biometric or not within seconds. All you have to do is look at the front cover of your passport. If you see a small gold rectangle with a circle in the middle, that is a biometric passport symbol.

Source: Photoaid Official Website
✅If you see the symbol, you have a biometric/e-passport.
❌If you don’t see it, it is likely to be an older or a non-biometric passport.
Good to know:
- All current US passports now issued are biometric.
- If your passport is old and doesn’t have the symbol, you can still use it until it expire. However, you may be directed to manual immigration lines instead of automated gates.
Biometric Passport Chip
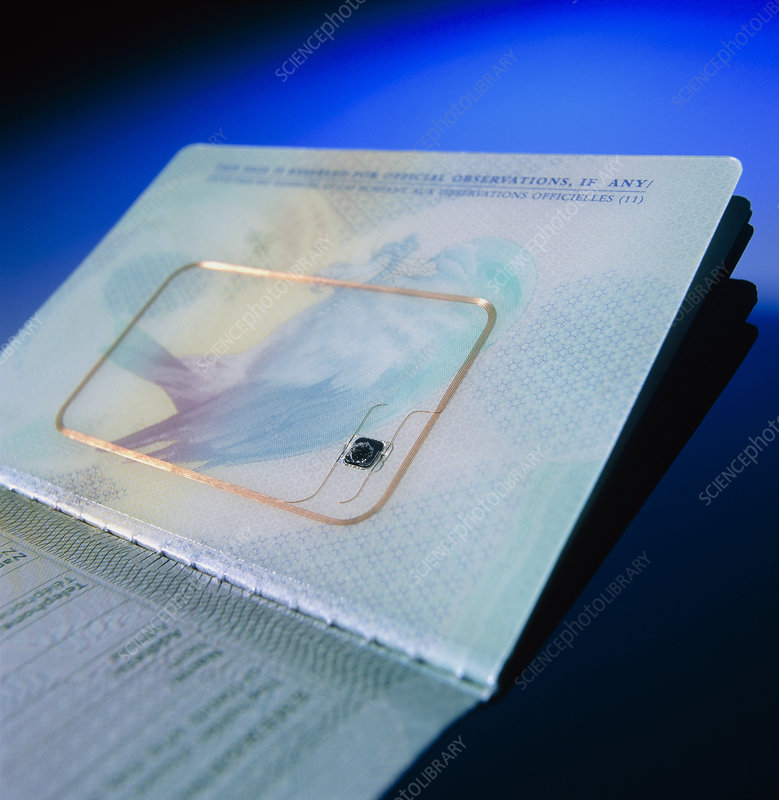

Source: Science Photo Library Official Website
The information stored in a Biometric Passport chip depends on your issuing country, but typically includes:
- Personal data: name, nationality, date of birth, passport number, expiry date
- Digital passport photo: used for facial recognition at border control
- Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) data: the two lines of characters at the bottom of your photo page
- Some countries also include:
- Fingerprints
- Iris templates (Retinal Scans)
- Additional facial data points
For example, US biometric passport chip stores your biographic data and a digital version of your photo. Other biometrics (like fingerprints) may be collected separately at the border for immigration for security purposes and are not stored in the chip itself. Furthermore, the format of the data in the biometric chip are standardized globally, meaning immigration systems all over the world will be able to read the chip in a standardized way.
Using Biometric Passport in Airports

Source: Washington Post, a travel article by Andrea Sachs
Manual inspection (classic passport control)
A border officer will:
- Look at your passport and photo
- Scan the chip to confirm that the passport is genuine
- Compare your face to the digital photo and printed photo
- Check your details against immigration databases and watchlists
Note: The chip helps to ensure that the document itself has not been tampered with or duplicated, making it harder for identity thefts to occur.
Automated e-gates and self-service kiosks
Many major airports now offer e-gates or self service kiosks for biometric passport holders:
- You place your passport on a reader so it can scan the chip
- A camera captures your face and compares it to the digital photo which is stored in the chip
- If it matches and there are no issues with your record, the gate opens and you’re through
Note: New or upgraded border systems in regions like Europe, where biometric verification is becoming standard for visitors all over the world.
Biometric Passports: Is it Safe?
WIth the world being more and more digitalized, people question the safety of having all information digitalized. With this biometric passport, they add several digital protection layers which is much safer than having all your information on paper.
Digital signatures and authenticity checks
The data on the chip is digitally signed by the issuing authority. When the chip is read:
- The system will check the digital signature to ensure the information hasn’t been changed.
- If someone tried to alter your photo or personal data, the signature would fail the check.
With that in mind, this protection makes it much harder for others to tamper with your passport or commit forgeries.
Fact: Some e-passports has a challenge and response mechanism where the chip proves that it holds a secret key without actually revealing it. This mechanism helps to prevent criminals from copying the chip and producing a duplicate of the passport.
Encrypted communication
Modern e-passport systems use encryption so that data exchanged between the chip and the reader is protected. That means if someone is nearby holding some kind of scanner, they can’t easily tap in and copy your information.
Privacy and tracking
There is this concern about whether or not someone can scan my passport through my bag. It is a common and typical concern, especially using biometric passports for the first time. I can tell you now that the chip is designed to be read at very short range with a proper reader. Therefore, identity theft is harder than you think!
Upgrading to Biometric Passports
If your passport is still valid but not biometric, you can still keep on using it until it expires. However, if you travel frequently or plan to visit countries or regions where uses a lot of e-gates and biometric checks, renewing your passports earlier may be a wise choice.
Biometric Passport FAQs
Is a biometric passport the same as an e-passport?
Yes. Terms like biometric passport, e-passport, and electronic passport all refer to a passport with an embedded chip storing your personal and biometric data.Does every country issue biometric passports now?
Not every single country, but the vast majority do. Most major travel destinations now issue biometric passports by default and build their border systems around them.Does a biometric passport store my fingerprints?
It depends on your country. Some countries store only your photo and basic details in the chip. Others also store fingerprint or iris data, especially in regions with advanced border systems. Even when fingerprints are collected at the border, they are not always stored in the passport chip itself.Are biometric passports safer than old passports?
Generally, yes. They combine physical security features (holograms, special inks, etc.) with digital protections (signed chip data, anti-cloning measures, encryption). This makes forgery and identity misuse significantly harder.Can someone track me with my biometric passport?
The chip doesn’t broadcast your location like a GPS device. It can only be read at very short range with specialized equipment, and security protocols limit what can be accessed without the data printed in your passport. Day-to-day, it’s not a realistic tracking device.





 NO.1
NO.1











