
Wondering whether Japan Plug Type is similar to the U.S.? Both Japan and the U.S. use type A and B, while the voltage is different. ✨Let's explore Japan Plug Type and prepare your Japan travel better!
Japan Plug Type vs U.S.
Both Japan and the U.S. use the the most common power outlets, Type A and Type B. So, visitors from the United States don't need adapters. Let's check what's the Type A and B to make sure!
Plug Type A & Type B
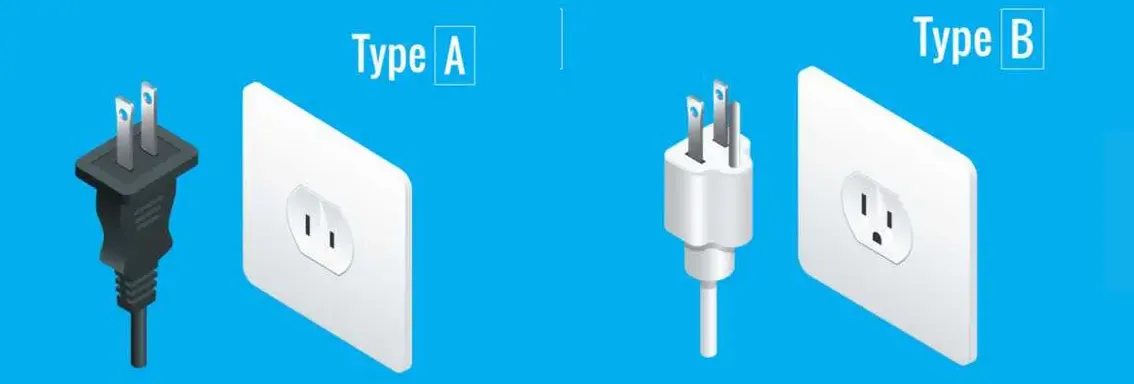
Japan primarily uses two types of electrical plugs, known as Type A and Type B. These plug types are also used in North America, Central America, and some other countries. Here's a detailed overview of the Japan plug types you will encounter:
Japan Plug Type | Description | Usage |
Type A Plug | An ungrounded plug with two flat parallel prongs | -The Type A plug is rated at 15 amps -In Japan, this plug is used for devices that do not require a ground connection. |
Type B Plug | A grounded plug with two flat parallel prongs and a grounding pin | -The Type B plug is rated at 15 amps -In Japan, this plug is used for devices that require grounding for safety. |
- Type A: Most Japanese outlets are Type A.
- Type B: While less common than Type A, Type B sockets can also be found in Japan, especially in newer buildings and facilities.
Voltage and Frequency - Japan vs U.S.

Here is the comparison of Voltage and Frequency between Japan and the U.S.:
Country | Voltage | Frequency |
Japan | 100 volts | 50 Hz in Eastern (Tokuo, Yokohama, Tohoku, and Hokkaido) 60 Hz in Western (Osaka, Kyoto, Nagoya, Hiroshima) |
The U.S. | 120 volts | 60 Hz |
*Note: Most equipment will not influenced by Frequency different.
How to deal with voltage difference?
1. Voltage Converter/Transformer: If your devices are not compatible with 100 volts that only suitable for 110 volts in the United States, you will need a voltage converter or transformer to step down the voltage to 100 volts.
2. Dual-Voltage Devices: Many modern electronic devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and camera chargers, are dual voltage, meaning they can operate on a range of voltages from 100 to 240 volts. For these devices, you don't need to consider voltage converter. But you should make sure your chargers are Type A or Type B.
✨If you're curious about how to stay connected in Japan, check the following Japan eSIM products!
Explore Cheap Japan eSIMs
Tips for Charging Your Devices in Japan

When traveling to Japan, you'll need voltage converter to charge your devices because the voltage is different from the United States. Here's tips for charging your devices:
Smartphones and Computers
Most modern smartphones, tablets, and laptops are built to support a wide voltage range (typically 100V to 240V). This means all you’ll need is a plug adapter to charge them in Japan without any issues
Hair Dryers
Take a moment to check whether your hair dryer is dual-voltage. If it is, simply switch it to the 100V setting and use it with a plug adapter. If not, your best bet is to either get a dual-voltage travel hair dryer or buy one locally in Japan that’s designed for the country’s 100V system.
USB Charger
For devices that rely on USB charging, a universal travel adapter with USB ports can be a real time-saver, letting you charge multiple gadgets at once without any hassle.
Power Strip
If you have several devices to charge at once, it might be a good idea to pack a power strip (just make sure it doesn’t have surge protection, as it might not work with the different voltage). Use it alongside a single adapter to plug it into the Japanese outlets.
❤️ Planning your Japan trip? Be sure to check out the article below for more tips and advice to help you prepare!
How Voltage and Frequency Differences Affect Devices in Japan

In Japan, the standard voltage supply is 100 volts, which is lower than 120 volts in the U.S.. The frequency is 50 Hz to 60 Hz. Here's how these voltage and frequency differences can affect devices:
Foreign Devices in Japan
If you're bringing devices from countries with higher voltage standards, like the U.S., they might not work as well when plugged into Japanese outlets. In some cases, a voltage transformer or power converter will be necessary to ensure they function correctly.
Frequency Difference
The varying frequencies can also cause issues, particularly with appliances that have motors or rely on precise timing. For instance, an electric clock built for 60 Hz may not keep accurate time when operated on 50 Hz. Similarly, appliances like fans, microwaves, or ovens may not work properly if the frequency doesn’t match.
Safety Concerns
Using devices with the wrong voltage can lead to safety risks such as electric shock, short-circuiting, or even fire hazards. Always check your device’s voltage specifications, and if needed, use the appropriate transformer or converter to avoid any potential issues.
👍 Tokyo Hotel Recommendations 👍
Where to Charge Your Devices Easily in Japan?

Charging your devices in Japan is relatively easy, as there are various options available. Here are some places where you can charge your devices:
1. Convenience Stores: Many convenience stores like 7-Eleven, FamilyMart, and Lawson have charging stations. Some may offer this service for free, while others might charge a small fee.
2. Cafés and Restaurants: Some cafés and restaurants provide power outlets for customers to use. Look for outlets near seating areas or ask the staff if it's okay to charge your device.
3. Train Stations: Major train stations often have charging stations or outlets available for public use. These can be found near seating areas or within waiting lounges.
4. Shopping Malls: Large shopping centers and department stores sometimes have charging stations or lockers where you can securely charge your phone while you shop.
5. Airports: Major Japan airports, including Haneda Airport and Kansai Airport, are equipped with numerous charging stations in the terminal areas.
FAQs about Japan Plug Type
What is the voltage and frequency used in Japan?
The standard voltage in Japan is 100 volts, which is lower than the U.S.. The frequency is 50 Hz in Eastern Japan (including Tokyo, Yokohama, Tohoku, and Hokkaido) and 60 Hz in Western Japan (including Osaka, Kyoto, Nagoya, Hiroshima).Do I need a voltage converter for my devices in Japan?
If your device is not rated for 100 volts and is not dual-voltage (100-240V), you will need a voltage converter to safely use it in Japan.Can I use my Type B plug in a Type A socket?
You can physically fit a Type B plug into a Type A socket because the two flat pins are the same. However, since Type A sockets in Japan are not grounded, the grounding pin on the Type B plug will not function.Is it safe to use electrical appliances in the bathroom?
As in many countries, it is generally not safe to use electrical appliances near water due to the risk of electric shock. Use appliances in the bathroom only if they are specifically designed for that environment and follow all safety instructions.

 27039 booked
27039 booked


